* For blog uploads you will want to choose a raster file format
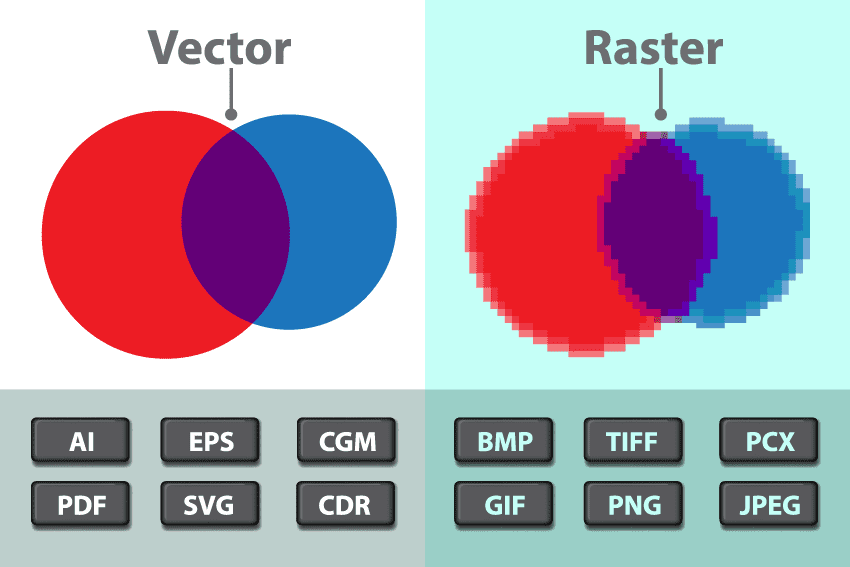
Raster vs. Vector Graphics Explained
Raster Graphics
Most images you see on your computer screen are raster graphics. Raster images use bit maps to store information. This means a large file needs a large bitmap. The larger the image, the more disk space the image file will take up. As an example, a 640 x 480 image requires information to be stored for 307,200 pixels, while a 3072 x 2048 image (from a 6.3 Megapixel digital camera) needs to store information for a whopping 6,291,456 pixels. We use algorithms which compress images to help reduce these file sizes. Image formats like jpeg and gif are common compressed image formats.
Scaling down these images is easy but enlarging a bitmap makes it pixelated or simply blurred. Hence for images which need to scaled to different sizes, we use vector graphics.
Raster file formats
JPG/JPEG- medium size, does not support transparencyJPG/JPEG is the most popular raster graphic file format using effective compression algorithms which enable you to achieve a small file size without quality loss (or with acceptable quality loss). When you save a JPG file you can select a compression level by adjusting the file quality to file size ratio. JPG is most commonly used on web pages (along with GIF and PNG).
GIF - small file size, supports transparencyA very well-known format is also GIF. As opposed to JPG, it is not used to save graphics/illustrations, not photos. The reason for that is the limited number of colors, i.e. 256, whereas JPG supports a full 24-bit palette (16.7 m colors).
PNG - small file size, supports transparency
TIF/TIFF - large file size, supports transparencyA format used basically only for printing. As opposed to JPG, only lossless compression is used in TIF files, which means their sizes are usually much larger. Instead, they contain much more additional information (paths, alpha channels, comments) that is used by printing devices.
BMP - old file format, not recommendedThe basic raster format, which is now rarely used. BMP files are unnecessarily large and additionally, they are not displayed by all Internet browsers.
Vector Graphics
AS a result a much smaller file is obtained.
Vector file formats
AI (Illustrator) Adobe Illustrators vector file format that stores all the data in an Illustrator file.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)A vector file format created with the Internet in mind and supported by Internet browsers (some require that an add-on be installed).
WMF/EMF (Windows MetaFile/Enhanced MetaFile)A Microsoft-created graphics file format containing both bitmaps and vectors.

No comments:
Post a Comment